| CPU | Arm Cortex-R4F |
| Frequency (MHz) | 160, 180 |
| ADC | 2 x 12-Bit (24ch) |
| GPIO | 58, 101 |
| UART | 2 |
| Number of I2Cs | 1 |
| Features | Hercules high-performance microcontroller |
| TI functional safety category | Functional Safety-Compliant |
| Operating temperature range (C) | -40 to 125 |
| Power supply solution | TPS65381A-Q1 |
- High-Performance Automotive-Grade Microcontroller for Safety-Critical Applications
- Dual CPUs Running in Lockstep
- ECC on Flash and RAM Interfaces
- Built-In Self-Test (BIST) for CPU and On-chip RAMs
- Error Signaling Module With Error Pin
- Voltage and Clock Monitoring
- ARM Cortex-R4F 32-Bit RISC CPU
- 1.66 DMIPS/MHz With 8-Stage Pipeline
- FPU With Single- and Double-Precision
- 12-Region Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- Open Architecture With Third-Party Support
- Operating Conditions
- Up to 180-MHz System Clock
- Core Supply Voltage (VCC): 1.14 to 1.32 V
- I/O Supply Voltage (VCCIO): 3.0 to 3.6 V
- Integrated Memory
- 1.25MB of Program Flash With ECC
- 192KB of RAM With ECC
- 64KB of Flash for Emulated EEPROM With ECC
- 16-Bit External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- Common Platform Architecture
- Consistent Memory Map Across Family
- Real-Time Interrupt (RTI) Timer (OS Timer)
- 128-Channel Vectored Interrupt Module (VIM)
- 2-Channel Cyclic Redundancy Checker (CRC)
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller
- 16 Channels and 32 Control Packets
- Parity Protection for Control Packet RAM
- DMA Accesses Protected by Dedicated MPU
- Frequency-Modulated Phase-Locked Loop (FMPLL) With Built-In Slip Detector
- Separate Nonmodulating PLL
- IEEE 1149.1 JTAG, Boundary Scan and ARM CoreSight Components
- Advanced JTAG Security Module (AJSM)
- Calibration Capabilities
- Parameter Overlay Module (POM)
- 16 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Pins Capable of Generating Interrupts
- Enhanced Timing Peripherals for Motor Control
- 7 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM) Modules
- 6 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Modules
- 2 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP) Modules
- Two Next Generation High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
- N2HET1: 32 Programmable Channels
- N2HET2: 18 Programmable Channels
- 160-Word Instruction RAM Each With Parity Protection
- Each N2HET Includes Hardware Angle Generator
- Dedicated High-End Timer Transfer Unit (HTU) for Each N2HET
- Two 12-Bit Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converter (MibADC) Modules
- ADC1: 24 Channels
- ADC2: 16 Channels Shared With ADC1
- 64 Result Buffers Each With Parity Protection
- Multiple Communication Interfaces
- FlexRay Controller With 2 Channels
- 8KB of Message RAM With Parity Protection
- Dedicated FlexRay Transfer Unit (FTU)
- Three CAN Controllers (DCANs)
- 64 Mailboxes Each With Parity Protection
- Compliant to CAN Protocol Version 2.0A and 2.0B
- Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- Three Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface (MibSPI) Modules
- 128 Words Each With Parity Protection
- 8 Transfer Groups
- Up to Two Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Modules
- Two UART (SCI) Interfaces, One With Local Interconnect Network (LIN 2.1) Interface Support
- FlexRay Controller With 2 Channels
- Packages
- 144-Pin Quad Flatpack (PGE) [Green]
- 337-Ball Grid Array (ZWT) [Green]
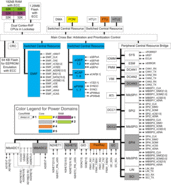
The TMS570LS1225 device is a high-performance automotive-grade microcontroller family for safety systems. The safety architecture includes dual CPUs in lockstep, CPU and memory BIST logic, ECC on both the flash and the data SRAM, parity on peripheral memories, and loopback capability on peripheral I/Os.
The TMS570LS1225 device integrates the ARM Cortex-R4F floating-point CPU which offers an efficient 1.66DMIPS/MHz, and has configurations which can run up to 180 MHz providing up to 298 DMIPS. The device supports the word-invariant big-endian [BE32] format.
The TMS570LS1225 device has 1.25MB of integrated flash and 192KB of data RAM with single-bit error correction and double-bit error detection. The flash memory on this device is a nonvolatile, electrically erasable and programmable memory, implemented with a 64-bit-wide data bus interface. The flash operates on a 3.3-V supply input (same level as I/O supply) for all read, program, and erase operations. When in pipeline mode, the flash operates with a system clock frequency of up to 180 MHz. The SRAM supports single-cycle read and write accesses in byte, halfword, word, and double-word modes throughout the supported frequency range.
The TMS570LS1225 device features peripherals for real-time control-based applications, including two Next Generation High-End Timer (N2HET) timing coprocessors with up to 44 I/O terminals, seven Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM) modules with up to 14 outputs, six Enhanced Capture (eCAP) modules, two Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP) modules, and two 12-bit Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) supporting up to 24 inputs.
The N2HET is an advanced intelligent timer that provides sophisticated timing functions for real-time applications. The timer is software-controlled, using a reduced instruction set, with a specialized timer micromachine and an attached I/O port. The N2HET can be used for pulse-width-modulated outputs, capture or compare inputs, or general-purpose I/O (GIO). The N2HET is especially well suited for applications requiring multiple sensor information and drive actuators with complex and accurate time pulses. A High-End Timer Transfer Unit (HTU) can perform DMA-type transactions to transfer N2HET data to or from main memory. A Memory Protection Unit (MPU) is built into the HTU.
The ePWM module can generate complex pulse width waveforms with minimal CPU overhead or intervention. The ePWM is easy to use and it supports both high-side and low-side PWM and deadband generation. With integrated trip zone protection and synchronization with the on-chip MibADC, the ePWM module is ideal for digital motor control applications.
The eCAP module is essential in systems where the accurately timed capture of external events is important. The eCAP can also be used to monitor the ePWM outputs or for simple PWM generation when the eCAP is not needed for capture applications.
The eQEP module is used for direct interface with a linear or rotary incremental encoder to get position, direction, and speed information from a rotating machine as used in high-performance motion and position-control systems.
The device has two 12-bit-resolution MibADCs with 24 total inputs and 64 words of parity-protected buffer RAM each. The MibADC channels can be converted individually or can be grouped by software for sequential conversion sequences. Sixteen inputs are shared between the two MibADCs. Each MibADC supports three separate groupings of channels. Each group can be converted once when triggered or configured for continuous conversion mode. The MibADC has a 10-bit mode for use when compatibility with older devices or faster conversion time is desired. MibADC1 also supports the use of external analog multiplexers.
The device has multiple communication interfaces: three MibSPIs, two SPIs, one LIN, one SCI, three DCANs, one I2C, and one FlexRay controller with two channels. The SPI provides a convenient method of serial high-speed communications between similar shift-register type devices. The LIN supports the Local Interconnect standard 2.0 and can be used as a UART in full-duplex mode using the standard Non-Return-to-Zero (NRZ) format. The DCAN supports the CAN 2.0 (A and B) protocol standard and uses a serial, multimaster communication protocol that efficiently supports distributed real-time control with robust communication rates of up to 1 Mbps. The DCAN is ideal for systems operating in noisy and harsh environments (for example, automotive and industrial fields) that require reliable serial communication or multiplexed wiring. The FlexRay controller uses a dual-channel serial, fixed time base multimaster communication protocol with communication rates of 10 Mbps per channel. A FlexRay Transfer Unit (FTU) enables autonomous transfers of FlexRay data to and from main CPU memory. Transfers are protected by a dedicated, built-in MPU.
The I2C module is a multimaster communication module providing an interface between the microcontroller and an I2C-compatible device through the I2C serial bus. The I2C supports speeds of 100 and 400 Kbps.
A Frequency-Modulated Phase-Locked Loop (FMPLL) clock module is used to multiply the external frequency reference to a higher frequency for internal use. The Global Clock Module (GCM) manages the mapping between the available clock sources and the device clock domains.
The device also has an External Clock Prescaler (ECP) module that when enabled, outputs a continuous external clock on the ECLK terminal. The ECLK frequency is a user-programmable ratio of the peripheral interface clock (VCLK) frequency. This low-frequency output can be monitored externally as an indicator of the device operating frequency.
The Direct Memory Access (DMA) controller has 16 channels, 32 control packets, and parity protection on its memory. An MPU is built into the DMA to protect memory against erroneous transfers.
The Error Signaling Module (ESM) monitors all device errors and determines whether an interrupt or external error pin (ball) is triggered when a fault is detected. The nERROR terminal can be monitored externally as an indicator of a fault condition in the microcontroller.
The External Memory Interface (EMIF) provides a memory extension to asynchronous and synchronous memories or other slave devices.
A Parameter Overlay Module (POM) enhances the calibration capabilities of application code. The POM can reroute flash accesses to internal memory or to the EMIF, thus avoiding the reprogramming steps necessary for parameter updates in flash.
With integrated safety features and a wide choice of communication and control peripherals, the TMS570LS1225 device is an ideal solution for high-performance real-time control applications with safety-critical requirements.